Sacroiliac Joint Pain
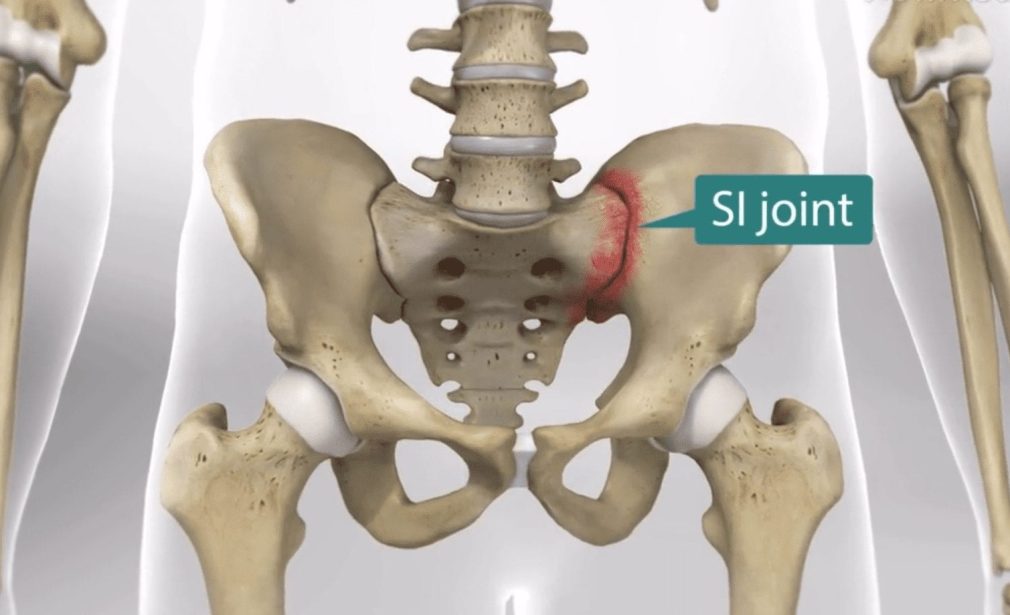
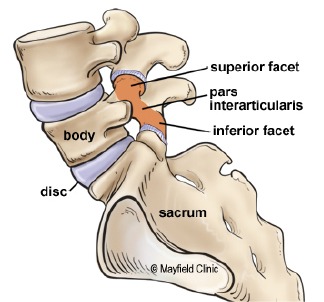
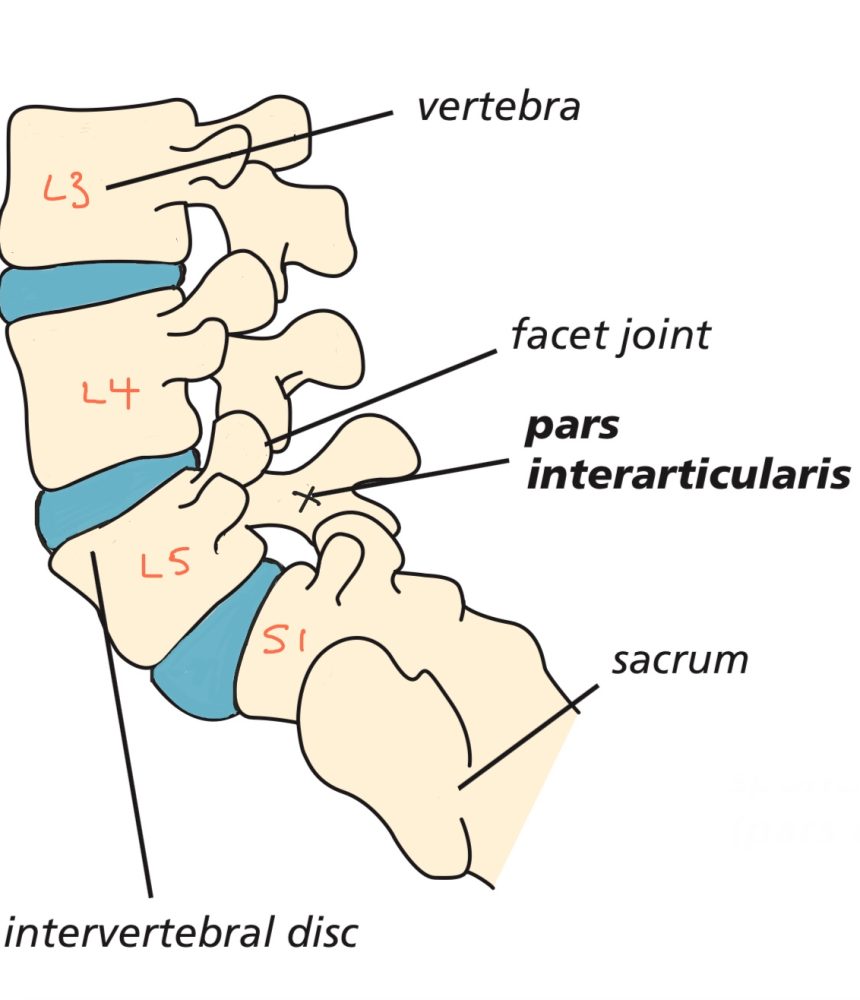
Sacroiliac joint pain refers to discomfort or pain in the sacroiliac joints, which are located at the base of the spine where the sacrum (the triangular bone at the base of the spine) and the ilium (the large pelvic bone) meet. The sacroiliac joints are essential for transferring the weight of the upper body to the pelvis and legs and play a crucial role in providing stability and absorbing shock during movement. Pain in this region can arise from various causes, and sacroiliac joint dysfunction is a common source of lower back pain.

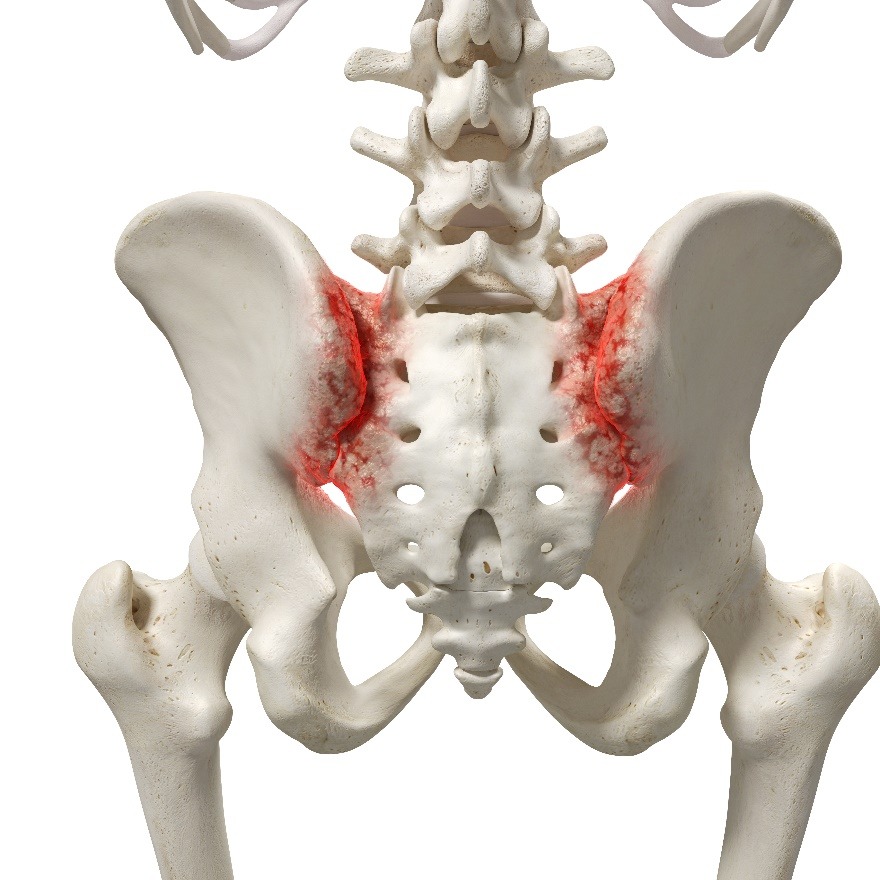
Key Features of Sacroiliac Joint Pain:
Causes:
Inflammation: Inflammatory conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis or arthritis can cause inflammation in the sacroiliac joints.
Trauma: Injury or trauma, such as a fall, can lead to sacroiliac joint pain.
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause increased mobility in the sacroiliac joints, leading to pain.
Degeneration: Wear and tear on the joint surfaces due to aging can contribute to pain.
Symptoms:
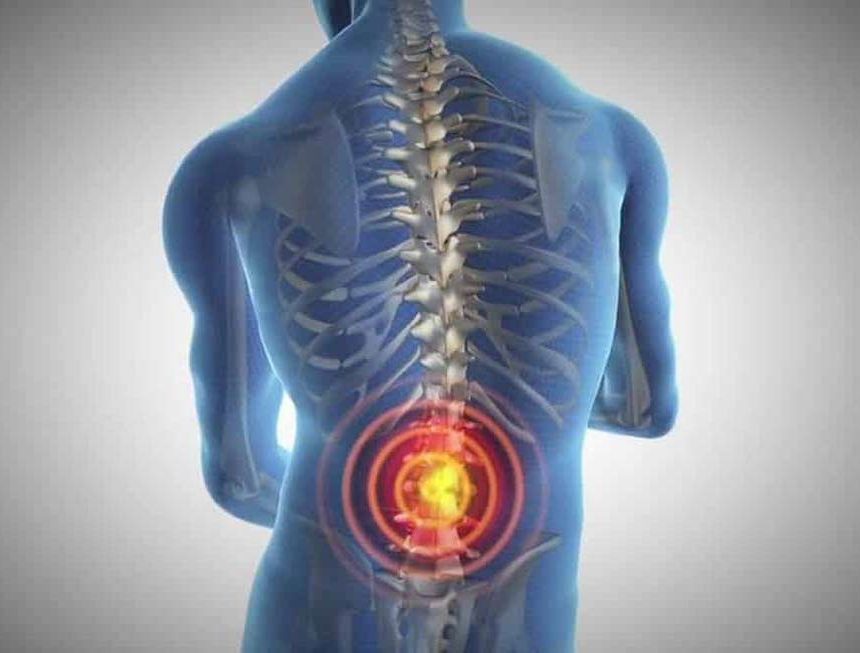
Low Back Pain: Pain is typically felt on one side of the lower back, near the buttocks.
Pain Radiation: Pain may radiate down into the buttocks, thighs, or even the groin.
Worsened with Activity: Pain may worsen with certain activities, such as walking, standing, or climbing stairs.
Changes in Sitting or Standing: Discomfort may be felt when transitioning between sitting and standing positions.
Stiffness: Stiffness and a sense of reduced flexibility in the lower back.
Diagnostic Approaches:
Physical Examination: A healthcare provider may perform various maneuvers to assess tenderness, range of motion, and pain in the sacroiliac joints.
Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), or CT (Computed Tomography) scans may be used to visualize the sacroiliac joints and identify abnormalities.
Diagnostic Injections: A diagnostic injection of a local anesthetic into the sacroiliac joint can help confirm if it is the source of pain.
Treatment Options:
Conservative Management:
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain.
Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve the strength and flexibility of the muscles supporting the sacroiliac joint.
Medications: Over-the-counter or prescription medications to manage pain and inflammation.
Joint Injections: Injections of corticosteroids into the sacroiliac joint for pain relief and to reduce inflammation.
Radiofrequency Ablation: A procedure involving the use of heat to disrupt nerve signals and provide longer-lasting pain relief.
Surgical Intervention: In rare cases where conservative measures are ineffective, surgical fusion of the sacroiliac joint may be considered.