Kyphoplasty
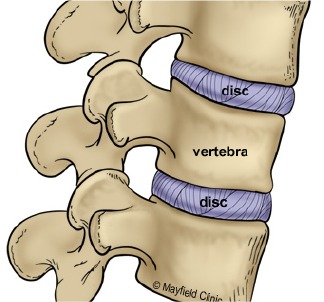

Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive surgical procedure designed to treat vertebral compression fractures, often caused by osteoporosis or trauma. The goal of kyphoplasty is to relieve pain, stabilize the fractured vertebra, and restore some of the lost vertebral height. Here is an overview of kyphoplasty for patients:
Indications:
Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures: Fractures in the spine due to weakened bones, often associated with osteoporosis.
Traumatic Vertebral Fractures: Fractures resulting from trauma or injury to the spine.
Preparation:
Medical Evaluation: Patients undergo a thorough medical evaluation, including imaging studies (X-rays, CT scans) to assess the extent of the vertebral compression fracture.
Discussion with Interventional Radiologist or Surgeon: The healthcare provider explains the procedure, discusses potential risks and benefits, and answers any questions the patient may have.
Procedure:
Positioning: The patient is typically positioned on their stomach or back on the operating table.
Local Anesthesia: A local anesthetic is applied to numb the skin and tissues at the site of the fracture.
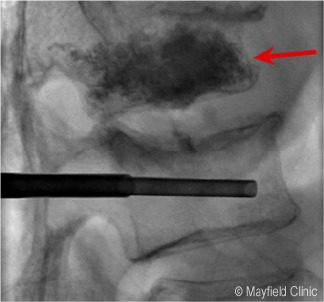
Guidance Imaging: Fluoroscopy (real-time X-ray) or other imaging techniques are used to guide the placement of instruments.
Needle Insertion: A small incision is made, and a hollow needle is inserted through the skin and into the fractured vertebra.
Balloon Inflation: A balloon-like device is inserted through the needle and inflated within the fractured vertebra to create a cavity.
Cement Injection: The cavity is filled with bone cement (usually a type of acrylic material), stabilizing the fracture and providing support.
Closure: The small incision is closed with a bandage or adhesive strips.
Recovery:
Observation: Patients are usually observed for a brief period after the procedure.
Pain Relief: Many patients experience immediate pain relief following kyphoplasty.
Return to Normal Activities: Patients are often able to resume normal activities within a short period.
Follow-up:
Postoperative Visits: Patients may have follow-up visits with their healthcare provider to monitor the healing process and assess the effectiveness of the procedure.
Imaging Studies: X-rays or other imaging studies may be conducted to evaluate the vertebral alignment and the distribution of the bone cement.
Potential Risks and Considerations:
Kyphoplasty is generally considered safe, but as with any medical procedure, there are risks, including infection, bleeding, or allergic reactions.
There is a risk of cement leakage, which can occur if the cement extends beyond the boundaries of the vertebral body.
Rare complications include nerve or spinal cord injury.